Understanding Enlarged Prostate: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Introduction
Prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition that affects many men as they age. This condition can lead to various urinary problems, impacting a person’s quality of life. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for an enlarged prostate.
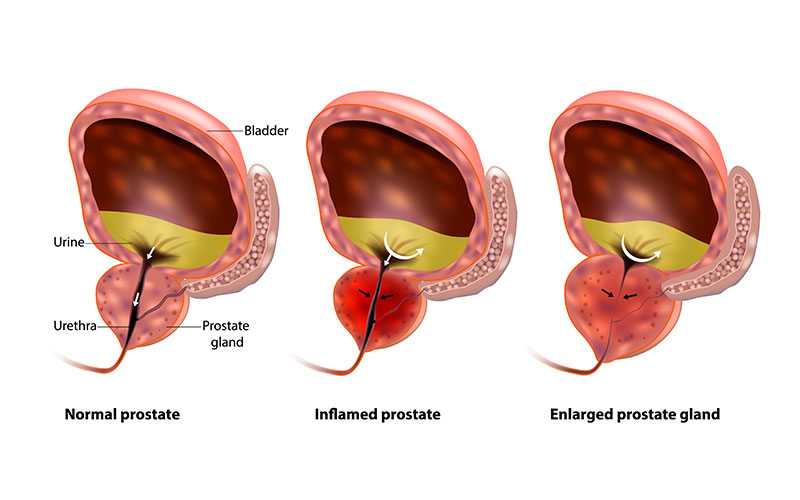
What is an Enlarged Prostate?
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland that plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. It surrounds the urethra, the tube responsible for carrying urine from the bladder out of the body. As men age, the prostate can grow in size, pressing against the urethra and causing a range of urinary symptoms.
Causes of Enlarged Prostate
The exact cause of an enlarged prostate is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development, including:
- Age: The risk of BPH increases with age, with the majority of men experiencing some degree of prostate enlargement by their 60s.
- Hormonal Changes: Changes in the balance of hormones, such as an increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are thought to play a role in prostate growth.
- Genetics: A family history of BPH may increase your risk of developing an enlarged prostate.
Common Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
An enlarged prostate can lead to various urinary symptoms, which may include:
- Frequent Urination: Needing to urinate more often, especially during the night.
- Urgency: Sudden and strong urges to urinate, making it challenging to hold it in.
- Weak Urine Stream: Difficulty starting and maintaining a steady urine flow.
- Incomplete Emptying: Feeling like the bladder is not completely emptied after urination.
- Dribbling: Leaking small amounts of urine after finishing urination.
- Straining: Effort is required to start urination.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options are available to manage an enlarged prostate, and the choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the patient’s preferences. Some of the common treatment options include:
- Watchful Waiting: For mild symptoms, a “watch and wait” approach may be suitable. Regular monitoring of symptoms is essential.
- Medications: There are various medications available that can help relieve symptoms, such as alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and laser therapy can alleviate symptoms by removing or shrinking excess prostate tissue.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical procedures like open prostatectomy or minimally invasive surgery may be necessary to remove a portion of the prostate.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
While you can’t prevent prostate enlargement entirely, you can take steps to manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise and a balanced diet can promote overall health and may help alleviate BPH symptoms.
- Limit Fluid Intake at Night: Reducing fluid intake in the evening can help minimize nighttime urination.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: These substances can irritate the bladder and worsen symptoms.
- Kegel Exercises: These exercises can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve bladder control.
Conclusion
Enlarged prostate, or benign prostatic hyperplasia, is a common condition that affects many men as they age. While it can cause troublesome urinary symptoms, there are various treatment options available to manage the condition and improve the quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of an enlarged prostate, it’s important to seek medical advice and explore the best treatment options to address this condition effectively.

