Kidney Transplant: A Lifesaving Treatment for Renal Health
Introduction:
Kidney transplant is a medical procedure that provides a new lease on life for individuals with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or severe kidney dysfunction. This transformative intervention involves replacing a failed kidney with a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor. This article explores the kidney transplant process, its benefits, and the post-transplant care essential for long-term success.
## Kidney Transplant Process:
### 1. **Evaluation and Eligibility:**
– Potential transplant recipients undergo a thorough medical and psychological evaluation to assess their overall health and suitability for the procedure.
### 2. **Donor Selection:**
– Living donors are typically family members or close friends, while deceased donors may be individuals who have chosen to donate their organs. Compatibility between donor and recipient is crucial for a successful transplant.
### 3. **Surgery:**
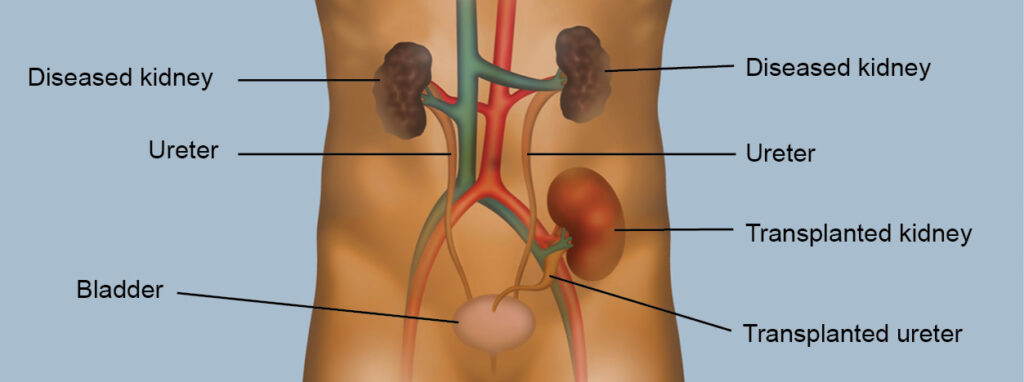
– The transplant surgery involves removing the diseased kidney and implanting the healthy kidney into the recipient’s lower abdomen. Blood vessels of the new kidney are connected to the recipient’s blood vessels, and the ureter is attached to the bladder.
### 4. **Immunosuppression:**
– Post-transplant, recipients are prescribed immunosuppressive medications to prevent the body from rejecting the new kidney. Regular monitoring and adjustment of these medications are crucial for long-term success.
## Benefits of Kidney Transplant:
1. **Improved Quality of Life:**
– Successful kidney transplants can restore normal kidney function, alleviating symptoms associated with ESRD, such as fatigue, nausea, and fluid retention.
2. **Reduced Dependency on Dialysis:**
– Transplantation often eliminates the need for dialysis, providing greater freedom and a more flexible lifestyle.
3. **Enhanced Long-Term Survival:**
– Kidney transplant recipients generally experience improved long-term survival rates compared to those on dialysis.
4. **Better Management of Comorbidities:**
– Transplantation may positively impact other health conditions associated with kidney failure, such as high blood pressure and anemia.
## Post-Transplant Care:
1. **Immunosuppressive Medications:**
– Lifelong adherence to immunosuppressive medications is crucial to prevent rejection of the transplanted kidney. Regular monitoring helps adjust medication dosages as needed.
2. **Regular Medical Check-ups:**
– Recipients undergo routine medical check-ups to monitor kidney function, blood pressure, and overall health. Early detection and intervention can prevent complications.
3. **Lifestyle Modifications:**
– Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, contributes to the overall well-being of transplant recipients.
4. **Psychological Support:**
– Kidney transplant recipients may face emotional challenges. Psychological support and counseling can help them cope with the changes and adjustments post-transplant.
## Potential Complications:
1. **Rejection:**
– The body’s immune system may recognize the transplanted kidney as foreign and attempt to reject it. Prompt detection and adjustment of medications can often prevent rejection.
2. **Infection:**
– Immunosuppressive medications may increase the risk of infections. Recipients are educated on infection prevention and receive vaccinations as needed.
3. **Side Effects of Medications:**
– Long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs may lead to side effects such as bone thinning and increased susceptibility to certain cancers. Regular monitoring helps manage these risks.
Conclusion:
Kidney transplant is a life-changing procedure that offers renewed hope and improved quality of life for individuals with advanced kidney disease. With advancements in medical technology and ongoing research, kidney transplantation continues to evolve, providing a beacon of hope for those in need of a second chance at a healthy and fulfilling life. Comprehensive post-transplant care and a collaborative approach between healthcare providers and recipients are pivotal for ensuring the long-term success of kidney transplants.